Application Layer
Application Layer Example
The Application Layer is the topmost layer in the OSI model, and it allows users to interact directly with the network through various applications. These could be web browsers, email clients, or file transfer utilities, among others.
This layer enables users to interact with the network through various applications like web browsers, email clients, and file transfer utilities.
Example: Watching Your Favorite Show on YouTube
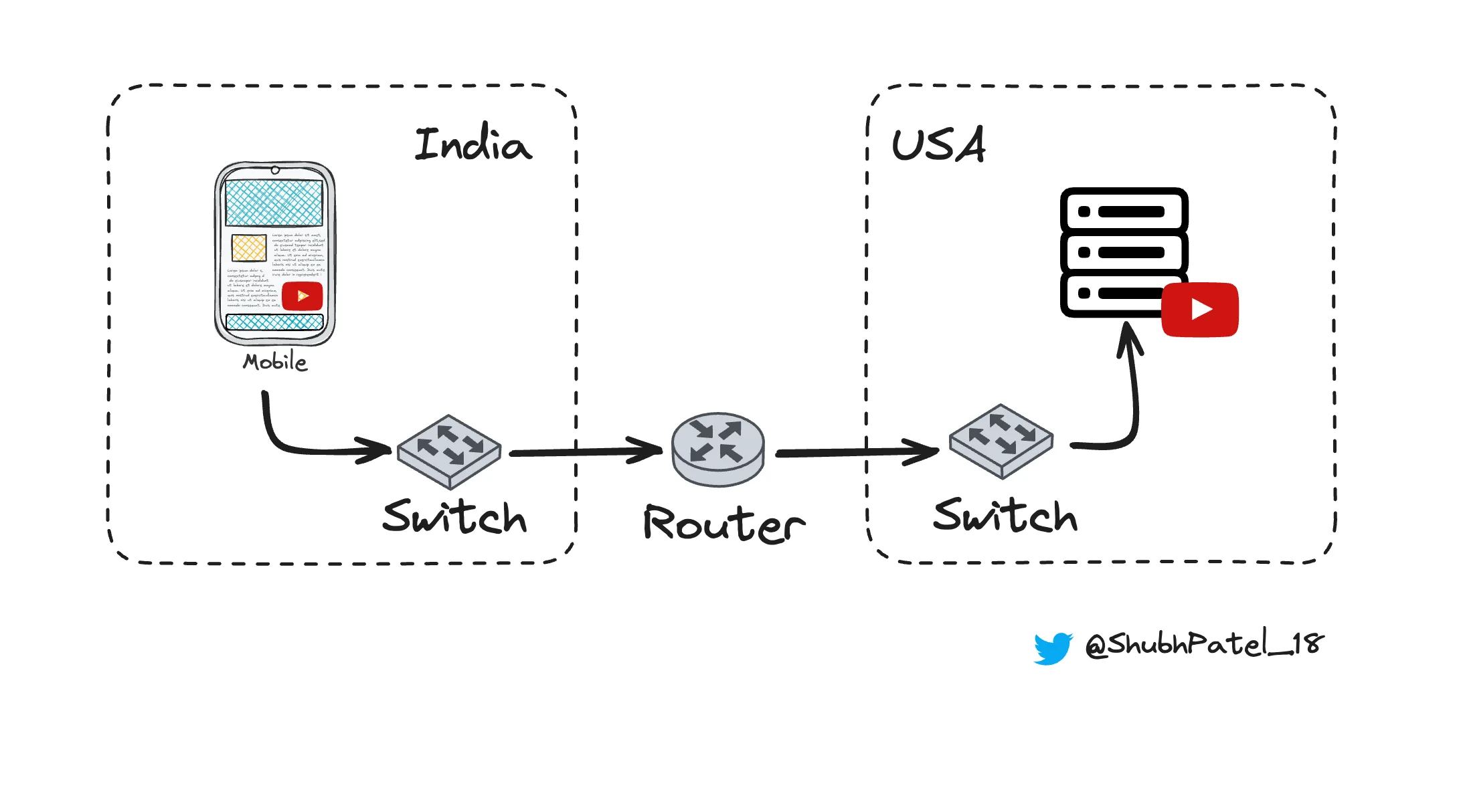
Imagine you missed your favorite TV show, but you know it will be uploaded to YouTube a few hours later. You live in India, and the YouTube servers hosting the video are in the US. To watch the video, you need to connect to the global network (the internet) through the application layer. Here’s how it works:
Step-by-Step Breakdown
Launching the YouTube App
-
You open the YouTube app on your smartphone. This app, provided by the application layer, serves as the interface, enabling you to connect to the internet and communicate with YouTube servers.
-
You type the name of your favorite show in the search bar and hit the search button.
Connecting to YouTube Servers
-
The YouTube app sends a request to the YouTube servers in the US to search for your show. This is where the application layer protocols come into play.
-
Protocols Used: The app uses the HTTP/HTTPS protocol to send and receive data. HTTPS ensures that the data transferred between your device and YouTube's servers is encrypted and secure.
Requesting the Video
-
Once the search results appear, you click on the video of your show. The YouTube app sends another HTTPS request to retrieve the video content from the server.
-
The request includes information like the video ID to ensure the correct content is delivered.
Formatting the Video Data
-
When the video is uploaded by the show owners, YouTube's servers format the video data into a streamable format. This involves encoding the video into multiple resolutions and bitrates to accommodate different internet speeds and device capabilities.
-
Data Handling: The application layer on YouTube's servers ensures the video is available in a format that can be efficiently streamed over the internet. This includes segmenting the video into small chunks and preparing it for adaptive streaming protocols.
Streaming the Video
-
The YouTube servers respond by sending the video data back to your device in India.
-
Protocols Used: Streaming protocols such as DASH (Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP) or HLS (HTTP Live Streaming) are employed to deliver the video in chunks, ensuring smooth playback and minimal buffering.
Conclusion
The application layer plays a crucial role in network communication by handling:
-
User Interface: Provides applications (like YouTube, Google Chrome) that allow users to interact with the internet seamlessly.
-
Data Formatting: Ensures data is formatted correctly for easy and efficient transmission.
-
Service Provision: Offers various services through applications, such as video streaming (YouTube) and app downloads (Play Store).
-
Protocol Support: Utilizes protocols (standards) like HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP to facilitate communication with servers and ensure data integrity and security.